Script Life Cycle
Reading this chapter takes about 15 minutes.
This chapter explains the lifecycle of scripts and its importance in the editor.
What is a Life Cycle?
The Life Cycle is the process of an object going from beginning to end.
The concept of the Life Cycle is widely used, especially in politics, economy, environment, technology, sociology, and many other fields. Its basic meaning can be commonly understood as the whole process of Cradle-to-Grave.
In the case of scripts, the Life Cycle represents the entire process of a script from Activate to Destroy and the process and order of execution of script functions in the code.
What Does a Script Life Cycle Include?
onStart( ) : void
When the script is instantiated, the onStart function is called before the first frame is updated.
Note: The editor will call the OnStart function on all scripts before calling functions such as OnUpdate for any script
onUpdate(dt : number) : void
The editor will call the onUpdate function once per frame of the game.
This is the main function used for frame updates.
Note: (dt : number) is the time interval, indicating the delay/seconds between the current frame and the previous frame
onDestroy( ) : void
This function is called after the last frame of script existence has been executed and after the onUpdate function has been executed.
bUseUpdate : boolean
Control whether the editor enables the onUpdate function call.
The default editor does not turn on the lifecycle of the script onUpdate, it needs to be called by the developer.
this. bUseUpdate = true;this. bUseUpdate = true;isRunningClient( ): boolean
Determine whether the current script is executed on the client side or on the server side.
For more information about the difference between the editor client and server, see the [Network Synchronization Structure and Mechanics] chapter.
Example Script:
@Component
export default class TestScript extends Script {
protected onStart(): void {
//Enable the OnUpdate function
this.useUpdate = true;
//Output to the console whether the current script is executing on the client
this.myLog(`The script is running client? ===> ${this.isRunningClient()}`);
if (this.isRunningClient()) { //Client===>
//Holding a cube object based on a GUID
let cube = Core.GameObject.find(`48A8055A40BBA143D723B19BDB2D21ED`);
this.myLog(`Into Client OnStart()`);
//Dispatch a delete cube event to the server and send the cube object to the server
Events.dispatchToServer("DeleteCube", cube);
}
else { //Server===>
this.myLog(`Into Server OnStart()`);
//Listening to the client delete cube event
Events.addClientListener("DeleteCube", (player, cube: Core.GameObject) => {
//Delete the cube object
cube.destroy();
});
}
}
protected onUpdate(dt: number): void {
if (this.isRunningClient()) {
this.myLog(`Into Client OnUpdate() > dTime:${dt}`);
}
else {
this.myLog(`Into Server OnUpdate() > dTime:${dt}`);
}
}
protected onDestroy(): void {
if (this.isRunningClient()) {
this.myLog(`Into Client OnDestroy()`);
}
else {
this.myLog(`Into Server OnDestroy()`);
}
}
public myLog(msg:string)
{
console.log(`TestLog ===> ${msg}`);
}
}@Component
export default class TestScript extends Script {
protected onStart(): void {
//Enable the OnUpdate function
this.useUpdate = true;
//Output to the console whether the current script is executing on the client
this.myLog(`The script is running client? ===> ${this.isRunningClient()}`);
if (this.isRunningClient()) { //Client===>
//Holding a cube object based on a GUID
let cube = Core.GameObject.find(`48A8055A40BBA143D723B19BDB2D21ED`);
this.myLog(`Into Client OnStart()`);
//Dispatch a delete cube event to the server and send the cube object to the server
Events.dispatchToServer("DeleteCube", cube);
}
else { //Server===>
this.myLog(`Into Server OnStart()`);
//Listening to the client delete cube event
Events.addClientListener("DeleteCube", (player, cube: Core.GameObject) => {
//Delete the cube object
cube.destroy();
});
}
}
protected onUpdate(dt: number): void {
if (this.isRunningClient()) {
this.myLog(`Into Client OnUpdate() > dTime:${dt}`);
}
else {
this.myLog(`Into Server OnUpdate() > dTime:${dt}`);
}
}
protected onDestroy(): void {
if (this.isRunningClient()) {
this.myLog(`Into Client OnDestroy()`);
}
else {
this.myLog(`Into Server OnDestroy()`);
}
}
public myLog(msg:string)
{
console.log(`TestLog ===> ${msg}`);
}
}Client Log:
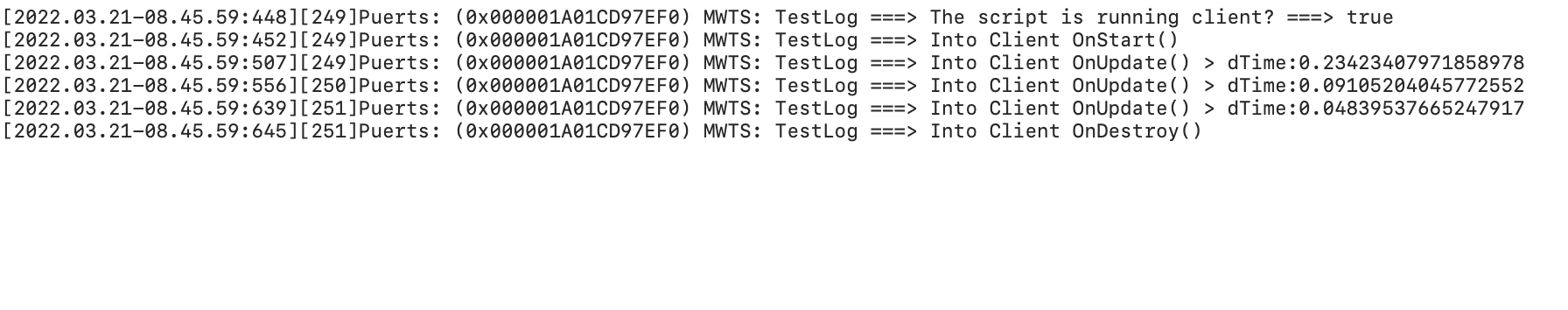
Server Log:
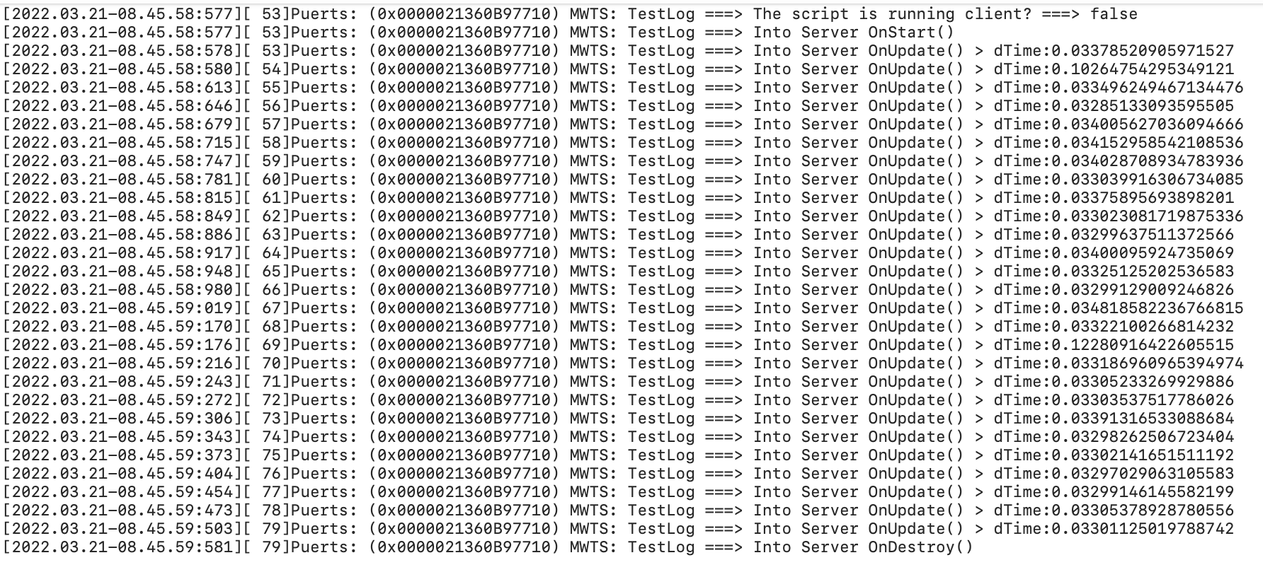
How to Properly Use Script Life Cycle?
Initialization
- The initialization of object properties (e.g., position, state, etc.) is usually made into a function that is executed in
onStart - Listening for events from the server or client, often written in the
onStartfunction
Example Script:
@Component
export default class TestScript extends Script {
//Declare some properties
public v3: Vector;
public level: number;
public name: string;
protected onStart(): void {
//Initialize properties in the first frame at the beginning of the game
this.initUser();
//Register event listeners at the first frame of the game start
this. initEvents();
}
//Functions for initializing properties
public initUser()
{
this.v3 = Type.Vector.ZERO;
this.level = 0;
this.name = `userName`;
}
//Initializing event listeners
public initEvents()
{
Events.addServerListener("eventName",parm);
}
}@Component
export default class TestScript extends Script {
//Declare some properties
public v3: Vector;
public level: number;
public name: string;
protected onStart(): void {
//Initialize properties in the first frame at the beginning of the game
this.initUser();
//Register event listeners at the first frame of the game start
this. initEvents();
}
//Functions for initializing properties
public initUser()
{
this.v3 = Type.Vector.ZERO;
this.level = 0;
this.name = `userName`;
}
//Initializing event listeners
public initEvents()
{
Events.addServerListener("eventName",parm);
}
}Rules of Thumb for the onUpdate Function
- Avoid writing loops in the
onUpdatefunction. Avoid infinite loops or empty references that can block program execution - Logic code should be written as functions to be called using
onUpdate, so that the code has good readability. - In the execution of the
onUpdatefunction, referenced objects should be nulled as much as possible. This improves the efficiency of locating problems, while avoiding empty references that can block program execution - If it is not necessary to use
onUpdate, try to use other functions instead. For example, you can usesetTimeoutto make timers for example. Only when you want to create a hit streak counter, the timer needs to be terminated or retimed, at this timesetTimeoutcannot meet the needs.
@Component
export default class TestScript extends Script {
/** if it's clickable */
isCanHit = true;
/** click cooldown */
hitCD:number = 2;
/** timer for controlling clicks */
canHitTimer:number = 0;
/** if it's a combo */
isCombo = false;
/** cooldown for an effective combo*/
comboCD = 5;
/** timer to control combos */
comboTimer:number = 0;
/** combo counter */
comboCount:number = 0;
/** maximum combo count */
maxComboCount:number = 0;
protected onStart(): void {
//enable the OnUpdate function
this.useUpdate = true;
}
protected onUpdate(dt: number): void {
//Check and time combos and clicks
this.checkHit_Combo(dt);
}
checkHit_Combo(dt: number)
{
if (!this.isCanHit) {
this.canHitTimer += dt;
if (this.canHitTimer >= this.hitCD) {
this.isCanHit = true;
this.canHitTimer = 0;
}
}
if (this.isCombo) {
this.comboTimer += dt;
if (this.comboTimer >= this.comboCD) {
this.comboTimer = 0;
this.comboCount = 0;
this.isCombo = false;
}
}
}
//when the user clicks
public hit()
{
if (this.isCanHit) {
this.canHitTimer = 0;
this.isCanHit = false;
if (this.isCombo) {
this.comboCount++;
this.comboTimer = 0;
if(this.comboCount >= this.maxComboCount)
{
this.comboCount = 0;
}
}
else {
this.comboTimer = 0;
this.comboCount = 0;
this.isCombo = true;
}
console.log(` this.comboCount ===> ${ this.comboCount}`);
}
}
}@Component
export default class TestScript extends Script {
/** if it's clickable */
isCanHit = true;
/** click cooldown */
hitCD:number = 2;
/** timer for controlling clicks */
canHitTimer:number = 0;
/** if it's a combo */
isCombo = false;
/** cooldown for an effective combo*/
comboCD = 5;
/** timer to control combos */
comboTimer:number = 0;
/** combo counter */
comboCount:number = 0;
/** maximum combo count */
maxComboCount:number = 0;
protected onStart(): void {
//enable the OnUpdate function
this.useUpdate = true;
}
protected onUpdate(dt: number): void {
//Check and time combos and clicks
this.checkHit_Combo(dt);
}
checkHit_Combo(dt: number)
{
if (!this.isCanHit) {
this.canHitTimer += dt;
if (this.canHitTimer >= this.hitCD) {
this.isCanHit = true;
this.canHitTimer = 0;
}
}
if (this.isCombo) {
this.comboTimer += dt;
if (this.comboTimer >= this.comboCD) {
this.comboTimer = 0;
this.comboCount = 0;
this.isCombo = false;
}
}
}
//when the user clicks
public hit()
{
if (this.isCanHit) {
this.canHitTimer = 0;
this.isCanHit = false;
if (this.isCombo) {
this.comboCount++;
this.comboTimer = 0;
if(this.comboCount >= this.maxComboCount)
{
this.comboCount = 0;
}
}
else {
this.comboTimer = 0;
this.comboCount = 0;
this.isCombo = true;
}
console.log(` this.comboCount ===> ${ this.comboCount}`);
}
}
}disconnectListener
Usually, we use a lot of addListener functions in onStart function or in UI scripts to listen to events. However, when the object corresponding to the script is destroyed, the events registered in the system are still not closed. Therefore, we add the logic to close the event listener in the onDestroy function in the life cycle.
Example Script:
@Component
export default class TestEvents extends Script {
//Declaring an array of events
myEvents = new Array<Events.EventListener>();
//Declare a count variable
public temp:number;
protected async onStart(): Promise<void> {
//Initialize count variable to 0
this.temp = 0;
//Holding a cube object based on a GUID
let cube = await Core.GameObject.find(`48A8055A40BBA143D723B19BDB2D21ED`);
//Add a local event listener and save the listener object to the event array
this.myEvents.push(Events.addLocalListener("TestEvent1",()=>{
console.log("========================>");
console.log(`this.temp ===> ${this.temp}`);
}));
//When the horizontal button '1' is pressed
this.myEvents.push(Events.onKeyDown(Type.Keys.One,()=>{
this.temp ++;
Events.dispatchLocal("TestEvent1");
}));
//When the horizontal button '2' is pressed
this.myEvents.push(Events.onKeyDown(Type.Keys.Two,()=>{
cube.destroy();
Events.dispatchLocal("TestEvent1");
}));
}
protected onDestroy(): void {
console.log(`Into OnDestroy()`);
//Iterate over all event objects and close all event listeners when the object is destroyed
this.myEvents.forEach(element => {
element.disconnect();
});
}
}@Component
export default class TestEvents extends Script {
//Declaring an array of events
myEvents = new Array<Events.EventListener>();
//Declare a count variable
public temp:number;
protected async onStart(): Promise<void> {
//Initialize count variable to 0
this.temp = 0;
//Holding a cube object based on a GUID
let cube = await Core.GameObject.find(`48A8055A40BBA143D723B19BDB2D21ED`);
//Add a local event listener and save the listener object to the event array
this.myEvents.push(Events.addLocalListener("TestEvent1",()=>{
console.log("========================>");
console.log(`this.temp ===> ${this.temp}`);
}));
//When the horizontal button '1' is pressed
this.myEvents.push(Events.onKeyDown(Type.Keys.One,()=>{
this.temp ++;
Events.dispatchLocal("TestEvent1");
}));
//When the horizontal button '2' is pressed
this.myEvents.push(Events.onKeyDown(Type.Keys.Two,()=>{
cube.destroy();
Events.dispatchLocal("TestEvent1");
}));
}
protected onDestroy(): void {
console.log(`Into OnDestroy()`);
//Iterate over all event objects and close all event listeners when the object is destroyed
this.myEvents.forEach(element => {
element.disconnect();
});
}
}Notes on Script Life Cycle
Enable the onUpdate Function
The value of useUpdate defaults to false
bUseUpdate must be manually changed to true for the onUpdate function to execute
Asynchronous Function
In onStart, we often use functions or syntax such as asynchronous seek
When using asynchronous, add the async flag to the function
Example: protected async onStart(): Promise<void> { }
 Editor Doc
Editor Doc